Is Biomethanol the Key to Carbon-Neutral Transportation?
As the world transitions toward cleaner energy sources, the transportation sector remains one of the most challenging areas to decarbonize. Amid growing concerns over climate change and carbon emissions, biomethanol has emerged as a promising solution. But is biomethanol the key to carbon-neutral transportation? Let’s explore its environmental benefits, economic viability, technological readiness, and future applications to find out.
What Is Biomethanol?
Biomethanol is a renewable fuel produced from organic biomass, including agricultural residues, forestry waste, and even municipal solid waste. Unlike traditional methanol derived from fossil fuels, biomethanol is made using sustainable resources, making it a cleaner and greener alternative.
Environmental Benefits of Biomethanol
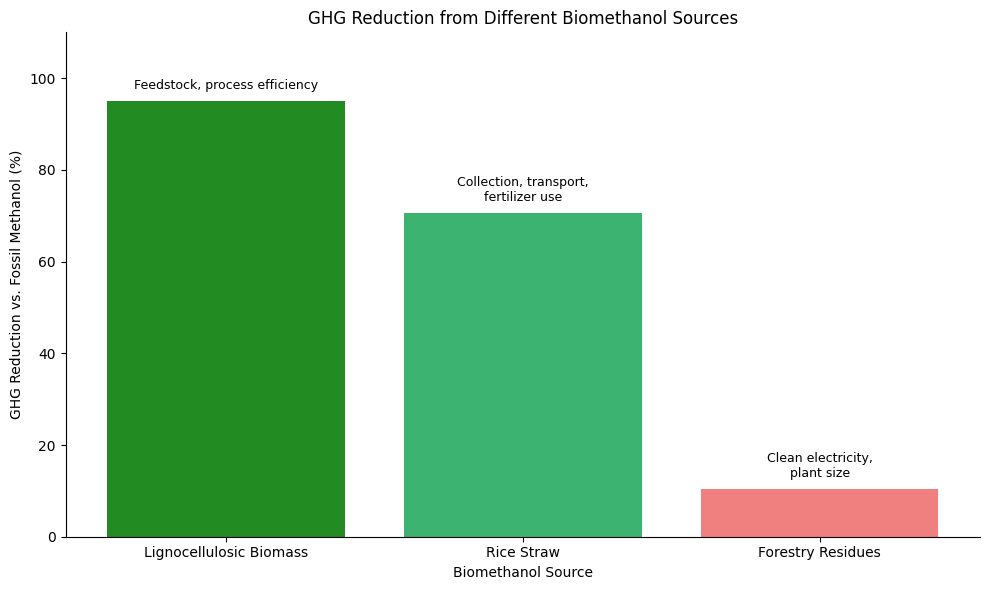
Biomethanol offers significant advantages in reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. When compared to conventional fossil fuels, biomethanol can lower carbon dioxide emissions by up to 95%. It also nearly eliminates sulfur oxide emissions and dramatically reduces nitrogen oxide levels, leading to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
In terms of life cycle emissions, biomethanol produced from sources like rice straw, forestry residues, or lignocellulosic biomass demonstrates superior performance. Clean electricity and optimized production processes can further reduce its environmental impact, making it a strong candidate for carbon-neutral transportation.
Additionally, biomethanol blends well with diesel and biodiesel, offering immediate emission reductions without requiring major changes to existing engines or infrastructure.
Economic and Technological Viability
While biomethanol is environmentally friendly, its current production costs can be higher than fossil-based fuels. These costs are influenced by the type of feedstock, plant size, and the use of renewable hydrogen in the production process. However, ongoing technological advancements and economies of scale are expected to make biomethanol increasingly cost-competitive.
Technologically, biomethanol is already a mature and scalable option. Innovations such as hydrothermal gasification and integration with renewable energy sources are driving down emissions and production costs. Biomethanol also offers better long-term potential than bioethanol for replacing gasoline, although it requires higher energy input during production.
Future Applications of Biomethanol
Biomethanol’s flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of transportation applications. It can power internal combustion engines and is already being used as a marine fuel. Its potential is especially high in sectors that are hard to electrify, such as aviation and shipping.
As countries seek sustainable alternatives for long-haul and heavy-duty transport, biomethanol stands out due to its compatibility with existing infrastructure and vehicles. Drop-in fuels made from captured carbon dioxide and renewable energy are also being developed, with biomethanol at the forefront of these innovations.
Challenges and Policy Support
Despite its advantages, the widespread adoption of biomethanol depends on several key factors:
- Cost Reduction: Continued innovation and larger-scale production are needed to lower costs.
- Infrastructure Investment: Upgrading supply chains and refueling stations will be essential.
- Policy Frameworks: Government support, subsidies, and carbon pricing will play a major role in accelerating adoption.
With the right policies and investments, biomethanol can scale up to meet the demands of global transportation and significantly reduce carbon emissions.
Conclusion: Is Biomethanol the Key to Carbon-Neutral Transportation?
Biomethanol is a strong contender in the race toward sustainable and carbon-neutral transportation. It offers substantial emission reductions, technological maturity, and versatility across various modes of transport. While economic and logistical challenges remain, the potential of biomethanol to reshape the future of mobility is clear.
As the world shifts toward greener solutions, biomethanol could very well be the key to carbon-neutral transportation—especially with continued innovation, supportive policy measures, and a collective push toward sustainability.