Energy, Economy, and Environment: Biomethanol from Rice Straw in China
Imagine mountains of agricultural waste that used to be a problem. Now, they can become a clean-burning fuel. This fuel powers vehicles and industries, cleans the air, and supports rural economies. This isn’t a distant dream but a growing reality in China. The country is turning its large amounts of rice straw into biomethanol. China produces a significant portion of the world’s rice, generating nearly 222 million tons of rice straw every year. In the past, much of this waste was disposed of by burning it. This practice had serious environmental consequences. However, a major change is happening. Biomethanol from rice straw is becoming a key part of China’s sustainable development plans. (Ran et al., 2023). This post will delve into China’s motivations for adopting this innovative method, the profound benefits it offers, its inspiring global implications, and the key Chinese companies at the forefront of this green revolution.
Why China Adopted This Method: A Multifaceted Approach
China’s pivot towards biomethanol from rice straw is driven by a convergence of critical environmental, energy security, and economic imperatives. It represents a pragmatic and visionary solution to several pressing national challenges.
Environmental Imperative: Cleaning the Air and Reducing Emissions
For decades, burning rice straw in open fields has significantly polluted the air in China, especially in farming areas. This practice releases large amounts of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and greenhouse gases into the air. This worsens smog, increases respiratory issues, and contributes to climate change. Biomethanol production provides a cleaner alternative. By turning rice straw into a liquid fuel, it removes the need for open burning, which reduces harmful emissions. Additionally, since rice plants absorb CO2 as they grow, using rice straw for biomethanol can be seen as carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative when paired with carbon capture technologies. This process effectively stores carbon that would otherwise be released.. China aims to peak CO2 emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060, driving the development of low-carbon energy policies (Yang & Lo, 2023).
Energy Security and Diversification: Less Reliance on Imports
China, as a rapidly developing and industrialized nation, faces the persistent challenge of ensuring energy security. Its considerable reliance on imported fossil fuels, particularly oil, creates vulnerabilities in its energy supply chain and subjects its economy to global price fluctuations. The domestic production of biomethanol from rice straw significantly enhances China’s energy independence. By converting an abundant, domestically available agricultural residue into a versatile fuel, China can reduce its reliance on external energy sources, thereby bolstering its national energy security. Biomethanol’s direct applicability in various sectors, especially transportation, allows for a strategic diversification of the energy mix, making the nation less susceptible to geopolitical disruptions affecting oil supplies.
Economic Benefits and Rural Development: Transforming Waste into Wealth
Beyond environmental and energy concerns, the biomethanol initiative offers significant economic advantages, especially for China’s large rural populations. Rice straw, once seen as waste with disposal costs, is now transformed into a valuable resource. This shift creates new income opportunities for farmers, enabling them to earn money from collecting and selling their agricultural residues. Setting up biomethanol production facilities in rural areas boosts local economies by generating jobs in feedstock collection, transportation, processing, and plant operation. Additionally, a useful byproduct of biomethanol production through anaerobic digestion is digestate. This nutrient-rich organic fertilizer can help reduce farmers’ reliance on costly chemical fertilizers. This improves agricultural sustainability while providing another financial benefit. The relationship between agriculture and energy production supports a strong circular economy in rural areas.
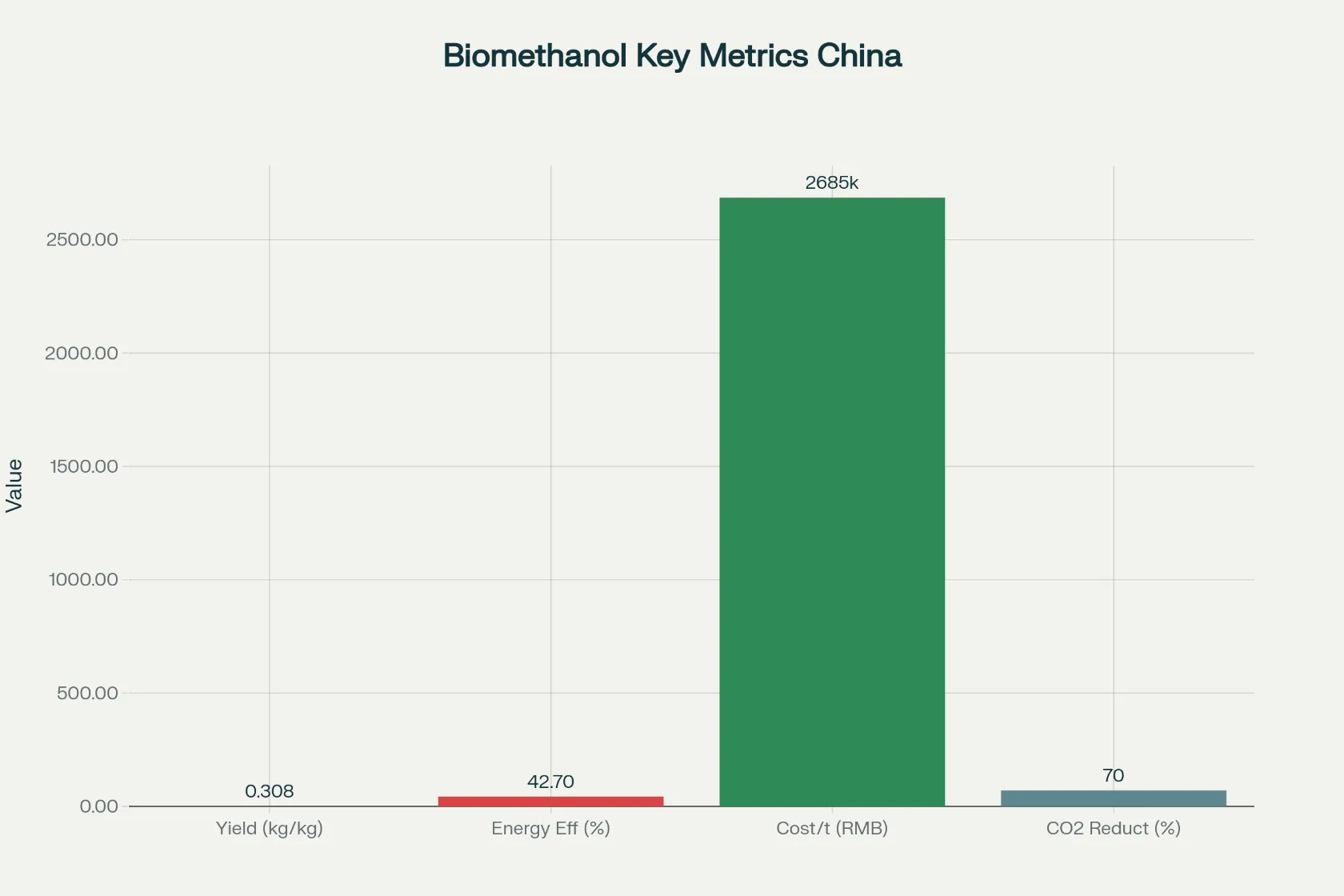
Biomethanol production from rice straw in China offers a sustainable solution. It meets energy needs, cuts greenhouse gas emissions, and effectively uses agricultural waste. Biomethanol yields are around 0.308 kg per kg of rice straw, and the energy efficiency is approximately 42.7% when using gasification technologies. This indicates that China has significant potential for bioenergy from rice straw. Currently, production costs are higher than those of fossil methanol, about 2,685 RMB per ton for a 50,000-ton plant. However, economic competitiveness should improve with policy support, technological innovation, and scaling up.
Using biomethanol from rice straw can reduce carbon emissions by over 70% compared to fossil-based methanol. It also helps decrease air pollution from open-field burning of straw. Improvements in process integration, like combining with renewable electricity, can further boost efficiency and lower lifecycle emissions. Overall, China’s biomethanol pathways show a mix of energy, economic, and environmental benefits Wang, et.al (2024). Continued innovation and supportive policies are essential for wider adoption and lower costs.
Inspiring the World: Global Implications of China’s Biomethanol Success
China is leading the way in scaling biomethanol production from rice straw. This initiative provides a strong and replicable example for other countries dealing with agricultural waste and shifting to renewable energy. The progress made has significant global implications for sustainable development for details..
China’s large agricultural sector and focused efforts on industrializing biomethanol production show that converting agricultural waste into valuable fuel is both possible and cost-effective. This serves as a powerful case study for other rice-producing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, which face similar challenges with agricultural residues and the related environmental and health issues.
China’s efforts also support several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action). By turning waste into energy and cutting down on pollution, China is showing a real commitment to a more sustainable future. The technological advancements, especially in biomass conversion methods like gasification and anaerobic digestion, being developed in China provide valuable insights and models that can be reused around the world. This encourages a quicker and more effective shift to sustainable energy sources everywhere. The process of converting rice straw into biomethanol reflects the principles of a circular economy. Here, waste is reduced, resources are continually reused, and value is generated from materials that would typically be thrown away.
For a broader understanding of global renewable energy trends and the potential of biomass energy, readers can explore reports from the International Energy Agency (IEA). The IEA regularly publishes comprehensive analyses on the evolving energy landscape, including detailed insights into bioenergy’s role in the global transition to clean energy. https://www.iea.org/
Chinese Companies Leading the Way in Biomethanol Production
The burgeoning biomethanol industry in China is propelled by a combination of established industrial giants and innovative clean energy companies. These enterprises are not only developing cutting-edge technologies but also forging strategic partnerships to scale up production and meet growing demand.
Among the prominent players, CIMC Enric Holdings Limited stands out for its significant involvement in constructing biomethanol plants. CIMC Enric, a leading intelligent manufacturer in the clean energy industry, has been instrumental in the development of crucial infrastructure for biomethanol production. They are actively engaged in constructing biomethanol facilities in China, with ambitious capacity targets to supply green methanol for various applications, including marine fuel. For more details on their clean energy initiatives, you can visit the CIMC Enric website or consult industry news regarding their green energy projects. (As of recent reports, CIMC Enric is constructing a biomethanol plant in Zhanjiang, Guangdong, targeting an initial annual production of 50,000 tonnes by late 2025, with plans to expand to 200,000 tonnes by 2027. You can find more information through reputable industry news sources that cover their clean energy ventures.)
Another major force in the sector is GoldWind Science & Technology Co., Ltd., a global leader in wind power solutions, which has expanded its portfolio to include biomethanol production. GoldWind has made headlines for its long-term agreements to supply green methanol, notably with shipping giant Maersk. This partnership underscores the growing demand for sustainable marine fuels and GoldWind’s commitment to large-scale green energy production. GoldWind’s innovative approach involves leveraging wind energy to produce both green bio-methanol and e-methanol, showcasing a holistic sustainable energy model. Their official website often features updates on their green energy projects. (GoldWind signed a landmark agreement with Maersk in November 2023 to supply 500,000 tonnes of green methanol annually, with production expected to begin in 2026 at a new facility in Hinggan League, Northeast China. More information can be found on GoldWind’s official news section or through maritime industry news outlets.)
Furthermore, ESGTODAY specializes in agricultural waste treatment, particularly in straw biogas plants and pretreatment technologies, which are foundational to efficient biomethanol production from rice straw. Their expertise in converting agricultural residues into biogas and further refining it into valuable resources positions them as a crucial enabler within this ecosystem. Their focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural waste management aligns perfectly with China’s biomethanol ambitions. You can explore their technologies at: https://www.esgtoday.com/maersk-signs-its-largest-ever-green-methanol-deal-to-drive-fleet-decarbonization/
These companies, alongside other emerging players and research institutions, are continually pushing the boundaries of technology and scaling up production, signaling a robust and dynamic future for biomethanol in China.
To gain further insights into the broader renewable energy industry in China and the specific contributions of these companies, reports from reputable financial news outlets or clean energy analysis firms can be highly informative.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While China’s biomethanol journey is inspiring, it’s not without its challenges. Logistical hurdles in collecting and transporting vast quantities of diffuse rice straw, the initial capital investment required for large-scale plants, and the ongoing need for technological refinement to optimize conversion efficiency remain important considerations. However, the immense potential of biomethanol from rice straw for China and the world far outweighs these challenges. Continuous research and development, coupled with strong government policy support and private sector investment, are paving the way for further innovation and expansion. This includes advancements in enzyme technologies, more efficient gasification processes, and improved integration with existing infrastructure.
Conclusion
China’s proactive embrace of biomethanol from rice straw represents a truly transformative approach to energy, economy, and environment. By converting what was once considered waste into a valuable, clean-burning fuel, China is not only addressing its own critical environmental concerns and enhancing energy security but also providing a powerful blueprint for sustainable development globally. The economic uplift for rural communities, coupled with the significant reduction in air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, underscores the multifaceted benefits of this innovation. As Chinese companies continue to lead the way in technological advancements and scale up production, their efforts serve as a beacon, inspiring a global shift towards a greener, more sustainable future powered by ingenuity and collaboration. The journey of rice straw to biomethanol in China is a testament to the power of human innovation in building a truly green future.
Citations
Yang, Y., & Lo, K. (2023). China’s renewable energy and energy efficiency policies toward carbon neutrality: A systematic cross-sectoral review. Energy & Environment, 0958305X2311674. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305×231167472
Ran, Y., Ghimire, N., Osman, A. I., & Ai, P. (2023). Rice straw for energy and value-added products in China: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01612-3
Reducing the lifecycle carbon emissions of rice straw-to-methanol for alternative marine fuel through self-generation and renewable electricity. Energy Conversion and Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2024.119202.
For a detailed life cycle analysis and insights on biomethanol production from corn straw in China, explore the comprehensive study at Biomethanol from Corn Straw in China: A Life Cycle Insight .

