Biomethanol: The Sustainable Future
Introduction to Biomethanol
Biomethanol, a renewable variant of methanol, is rapidly emerging as a cornerstone in the global transition to sustainable energy and chemical production. Unlike conventional methanol, which is primarily derived from fossil resources such as natural gas, biomethanol is produced from biomass feedstocks—ranging from agricultural residues and municipal solid waste to carbon dioxide captured from industrial processes.
With the chemical formula CH₃OH, methanol is a light, colorless, and biodegradable liquid that is highly soluble in water and widely used as a chemical feedstock, fuel, and energy carrier.
The growing urgency to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels has propelled biomethanol into the spotlight. Its production and use offer significant environmental benefits, including substantial reductions in carbon emissions and the potential for a closed carbon cycle when produced from waste streams or captured CO₂.
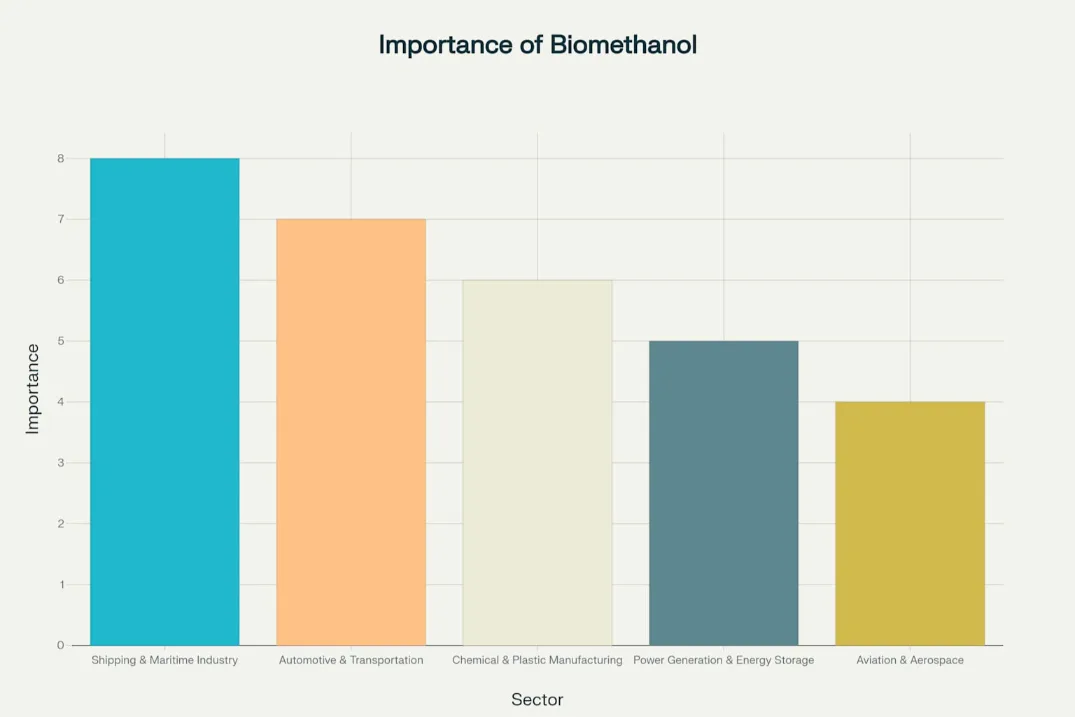
Shipping & Maritime Industry
The maritime industry, responsible for a substantial share of global emissions, is undergoing a profound transformation as it seeks cleaner alternatives to heavy fuel oil. Bio-methanol has emerged as a leading candidate for decarbonizing shipping operations due to its favorable environmental profile and operational compatibility.
Key Developments and Adoption
Engine Compatibility
Bio-methanol can be used in dual-fuel engines, enabling ships to switch between traditional marine fuels and methanol with minimal modifications. This flexibility accelerates adoption and reduces retrofitting costs.
Recent Milestones
Norway launched its first bio-methanol-powered feeder ship, the NCL Vestland, in April 2025—a significant step for sustainable maritime operations. Shipping giant Maersk has also expanded its fleet of methanol-enabled vessels.
Global Production
China is scaling up bio-methanol production with new plants dedicated to supplying the maritime sector, reflecting a global trend toward cleaner shipping fuels.
Advantages
Reduced Emissions: Bio-methanol significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional marine fuels, supporting International Maritime Organization (IMO) decarbonization targets.
Ease of Storage and Handling: Methanol is easier to store and handle than alternatives like hydrogen or ammonia, simplifying the transition for port infrastructure and ship operators.
Automotive & Transportation
Transportation accounts for nearly a quarter of global CO₂ emissions, making decarbonization of this sector a top priority. Biomethanol offers a practical and impactful solution, especially in applications where electrification is challenging or infrastructure is lacking.
Applications
Direct Fuel and Blending
Biomethanol can be used directly as a fuel or blended with gasoline to improve combustion efficiency and reduce emissions.
Fuel Additives
As a component in methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), biomethanol enhances fuel octane ratings and reduces harmful emissions.
Benefits
Lower Carbon Footprint: Biomethanol’s renewable origin means its lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions are significantly lower than those of fossil-derived fuels.
Economic Growth: The biomethanol fuel market is fostering new investment and job creation, particularly in regions rich in agricultural resources.
Chemical & Plastic Manufacturing
Methanol is a foundational building block in the chemical industry, serving as a precursor for a wide range of products including plastics, car parts, construction materials, textiles, and paints.
Sustainable Feedstock
Carbon Source
By sourcing carbon from biomass or recycled CO₂, chemical manufacturers can dramatically reduce environmental impact.
Drop-in Replacement
Renewable methanol is chemically identical to fossil-based methanol, allowing seamless integration into existing processes.
Emissions Reduction Potential
[Chart showing 95% emissions reduction compared to conventional methods]
Power Generation & Energy Storage
Beyond its role as a fuel and chemical feedstock, biomethanol is gaining attention as a versatile energy carrier for power generation and storage.
Innovative Processes
Biomass Conversion
Advanced technologies enable efficient transformation of agricultural residues into biomethanol and other valuable fuels.
Closed Carbon Cycle
By capturing and utilizing CO₂ generated during biomass fermentation, these processes create a closed-loop system.
Aviation & Aerospace
The aviation sector faces unique challenges in decarbonization due to the high energy density required for flight and limited alternatives to liquid fuels.
Production Pathways
Methanol-to-Jet (MTJ) Technology
Innovative catalytic processes convert biomethanol into jet fuel suitable for aviation use.
Feedstock Flexibility
Biomethanol can be produced from a wide variety of raw materials, enabling regional supply chains.
Future Outlook of Biomethanol
Biomethanol’s trajectory is closely tied to global efforts to decarbonize major industries and transition to a circular, low-carbon economy.
Scaling Production
Investments in new production facilities are rapidly increasing biomethanol availability.
Policy Support
Strong regulatory frameworks are accelerating market adoption across industries.
Technological Innovation
Advances in biomass conversion and CO₂ utilization are enhancing efficiency.
Conclusion
Biomethanol stands at the forefront of the renewable energy revolution, offering a versatile, scalable, and low-carbon alternative to fossil-derived methanol and fuels. Its applications span critical sectors—from shipping and transportation to chemicals, power, and aviation—delivering substantial environmental and economic benefits.
As innovation accelerates and markets mature, biomethanol is set to play a pivotal role in global decarbonization efforts, supporting the transition to a cleaner, more resilient, and sustainable energy future.
References & Further Reading
- ETIP Bioenergy: Biomethanol Production and Use as Fuel
- Ship Universe: Bio-Methanol Gains Momentum as Maritime Shipping Embraces Cleaner Fuels
- Market Research Intellect: From Bio to Drive – Biomethanol Fuels Lead the Charge in Eco Transport
- Carbon Recycling International: Chemicals and Plastics from Renewable Methanol
- SAE Mobilus: Advanced Biomass Conversion – Sustainable e-Methanol Production
- RISE: Methanol to Jet – Sustainable Aviation Fuel Production
Citations:
- https://ppl-ai-file-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/43017593/e210854b-5ec3-4357-a7e1-ca4a0c91aa9e/bmostafazadeh-Toxicology-V10-N3-29331-TE-RE-HL-First-edit-E-Hyperlink-final-Sh-SETE-Sh.pdf
- https://ppl-ai-file-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/43017593/9d36bb13-3b3f-474a-a228-5cc2ab8ec038/10.2478_vjbsd-2019-0011.pdf
- https://ppl-ai-file-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/43017593/952d4703-fb4e-4731-8c06-4eb31a7a541d/b7d6493e-9d61-435f-9fff-2ea044bdd627.pdf
- https://ppl-ai-file-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/43017593/b73416f7-0be4-4401-8fc6-6c8263b3129b/iaquaniello2017.pdf
- https://ppl-ai-file-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/43017593/23e07f7a-92f4-435b-a683-14329622abd0/svanberg2018.pdf

