15 Surprising Applications of Biomethanol You Didn’t Know Were Changing Your Daily Life
Biomethanol is quietly changing how we live, work, and move. Still, many people do not realize its wide and growing impact. It is a renewable form of methanol made from biomass, such as agricultural waste, municipal solid waste, or carbon dioxide. Biomethanol provides a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and offers significant environmental benefits. Along with hydrogen fuels, biomethanol plays a crucial role in the global shift toward cleaner energy and sustainable industry.
This blog examines 15 surprising ways biomethanol shapes your daily life, including transportation, manufacturing, energy, and even household products. Understanding these uses shows biomethanol’s versatility and its important role in creating a greener future.
What is Biomethanol?
Biomethanol, or renewable methanol, is chemically the same as conventional methanol (CH3OH). However, it comes from renewable sources instead of fossil fuels. It is a light, colorless, and biodegradable liquid that has a low carbon footprint. It often cuts greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% compared to fossil methanol.
Since it is a liquid at room temperature, biomethanol is easier to store and transport than gaseous fuels like hydrogen. This makes it a practical renewable energy carrier and chemical feedstock.
1. Renewable Fuel for Vehicles
Biomethanol can be used directly as a fuel or mixed with gasoline in internal combustion engines. Its high octane rating boosts engine performance and lowers emissions of pollutants such as NOx and particulate matter. It can also help produce biodiesel and other biofuels.
Why it matters:
- Reduces carbon emissions in transportation
- Works with existing fuel systems
- Supports sectors where electrification is difficult
2. Cleaner Marine Fuel
The shipping industry uses biomethanol as a low-emission marine fuel. Biomethanol cuts lifecycle CO₂ emissions by up to 95% compared to traditional marine fuels. It can also be used in dual-fuel engines, allowing ships to switch between methanol and conventional fuels.
Why it matters:
- Helps meet IMO and EU emissions goals
- Easier to store and handle than hydrogen or ammonia
- Being adopted by major shipping companies worldwide
3. Hydrogen Carrier and Storage Medium
Hydrogen fuels are vital for reducing emissions in many sectors, but they face challenges in storage and transport. Biomethanol serves as a liquid hydrogen carrier, chemically storing hydrogen and releasing it when necessary. This makes hydrogen distribution and use easier.
Why it matters:
- Solves hydrogen storage and transport issues
- Enables clean hydrogen use in transportation and industry
- Supports the developing hydrogen economy
Learn more about biomethanol solutions at Perpetual Next.
4. Feedstock for Chemical Industry
Biomethanol is a key renewable feedstock for making chemicals like formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl esters, and methylamines. These chemicals are critical in producing plastics, textiles, paints, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals.
Why it matters:
- Reduces reliance on fossil fuels in chemical production
- Encourages greener manufacturing processes
- Supports circular economy principles
5. Power Generation and Grid Balancing
Biomethanol is used as a renewable fuel in power plants and combined heat and power (CHP) systems. It provides flexible power to complement intermittent renewables like solar and wind, helping to stabilize the electricity grid.
Why it matters:
- Improves grid reliability
- Aids renewable energy integration
- Lowers emissions from power generation
6. Cooking and Heating Fuel
In many areas, biomethanol replaces traditional biomass fuels like wood or charcoal for cooking and heating. It burns cleanly, reducing indoor air pollution and the health risks that come with it.
Why it matters:
- Improves air quality and health outcomes
- Provides sustainable household energy
- Reduces deforestation and environmental harm
7. Solvent in Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Biomethanol is used as a solvent in making pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and personal care products. Its renewable origin lowers the environmental impact of these industries.
Why it matters:
- Supports green chemistry
- Reduces reliance on petrochemical solvents
- Enhances sustainability in consumer products
8. Antifreeze and Coolants
Methanol’s antifreeze qualities make biomethanol an eco-friendly alternative for automotive and industrial coolants. It helps prevent freezing and overheating in engines and machinery.
Why it matters:
- Offers biodegradable and less toxic antifreeze
- Lowers environmental pollution
- Encourages sustainable maintenance practices
9. Fuel Cells for Portable and Backup Power
Biomethanol powers direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs), which generate electricity for portable electronics, remote sensors, and emergency backup systems. This offers a clean and efficient power source.
Why it matters:
- Enables off-grid and emergency power
- Provides higher energy density than batteries in some instances
- Supports renewable energy use in various applications
10. Agricultural Inputs
Biomethanol is a feedstock for creating bio-based fertilizers and pesticides. This contributes to sustainable agriculture by reducing dependence on fossil-based chemicals.
Why it matters:
- Lowers the environmental effects of farming inputs
- Promotes a circular bioeconomy using agricultural waste
- Improves soil health and crop yields sustainably
11. Aviation Fuel Additive
Research is looking into biomethanol as a component in sustainable aviation fuels (SAF). This aims to cut the carbon footprint of air travel by blending with conventional jet fuel.
Why it matters:
- Addresses emissions in hard-to-decarbonize aviation
- Compatible with existing fuel systems
- Helps achieve global aviation climate targets
12. Plastic and Polymer Production
Biomethanol is a building block for bio-based plastics and polymers, providing renewable alternatives to petroleum-based materials.
Why it matters:
- Lowers the plastic industry’s carbon footprint
- Allows for biodegradable and recyclable plastics
- Supports a circular materials economy
13. Renewable Dimethyl Ether (DME) Production
Biomethanol can be turned into dimethyl ether, a clean-burning fuel used for heating, transportation, and as an aerosol propellant.
Why it matters:
- Offers a versatile, low-emission fuel
- Can replace diesel and LPG in many uses
- Expands renewable fuel options
14. Wastewater Treatment
Biomethanol acts as a carbon source in biological wastewater treatment. It helps promote denitrification and reduces nitrogen pollution that leads to toxic algal blooms.
Why it matters:
- Improves water quality
- Provides a renewable alternative to fossil methanol in treatment
- Supports sustainable urban infrastructure
For more technical details, see this scientific study on biomethanol applications.
15. Laboratory and Industrial Research
Biomethanol is commonly used as a solvent and reagent in labs and industrial research. This enables sustainable scientific innovation.
Why it matters:
- Cuts the environmental impact of research
- Encourages green chemistry principles
- Aids in the development of renewable technologies
Biomethanol and Hydrogen Fuels: Partners in the Renewable Energy Shift
While biomethanol is a versatile liquid fuel and chemical feedstock, hydrogen fuels complement it by providing zero-emission energy for sectors that are hard to electrify. Biomethanol’s role as a hydrogen carrier connects current infrastructure with the upcoming hydrogen economy. This allows for cleaner transport, industry, and power generation.
Together, biomethanol and hydrogen fuels form a powerful pair speeding up the global transition to sustainable energy.
Why Biomethanol Deserves More Attention
Even with its many applications and environmental benefits, biomethanol is often less recognized than electric vehicles or hydrogen fuels. Its compatibility with existing infrastructure, significant emissions reductions, and various industrial uses make it a practical and scalable solution for cutting emissions.
As governments and industries work toward net-zero targets, biomethanol’s importance will only increase, making it a key element in the future of renewable energy.
Learn more about renewable methanol applications from industry experts.
Conclusion: Biomethanol Is Already Changing Your Life
From powering vehicles and ships to enabling cleaner manufacturing and enhancing household energy, biomethanol is deeply woven into modern life. Along with hydrogen fuels, it plays an important role in the sustainable energy transition, offering real solutions across different sectors.
Recognizing these 15 surprising applications shows biomethanol’s true potential and highlights the need to support its development and use worldwide.
Explore Biomethanol Solutions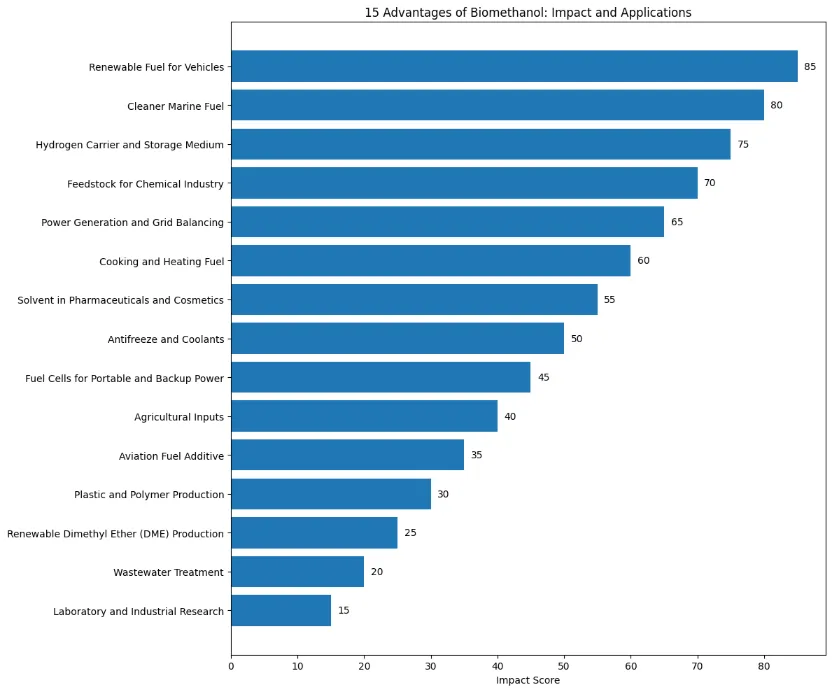
The Biomethanol Advantage: How Small Businesses Are Cutting Emissions While Boosting Profits
Discover how small enterprises are leveraging biomethanol to save money and reduce emissions.
Why Major Investors Are Quietly Pouring Billions into Biomethanol
Explore why big money is flowing into the biomethanol industry and what it means for the future.
Backlinks for Biomethanol Applications Blog
- Perpetual Next – Biomethanol Overview : Explains how biomethanol is used in everyday products like plastics, paints, and cosmetics.
- Springer – Biomethanol Production & Applications : A peer-reviewed article detailing biomethanol’s role in transportation, cooking, and industrial boilers.
- Methanol Institute – Renewable Methanol : Covers biomethanol’s environmental benefits and its use in fuels, chemicals, and consumer goods.

