Investing in Biomethanol: Early Stage Opportunities in a Rapidly Expanding Green Sector (2025 Update)
As the world accelerates its shift toward sustainable energy, biomethanol has emerged as a standout opportunity for investors
What is Biomethanol?
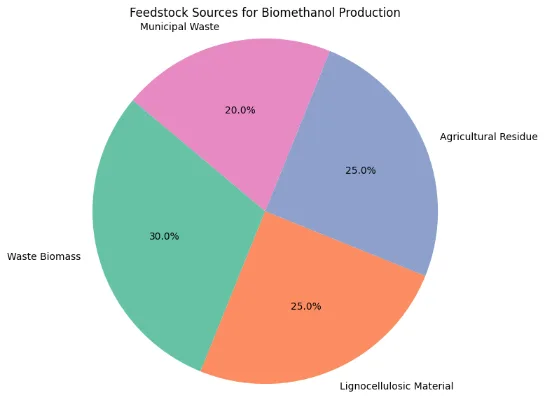
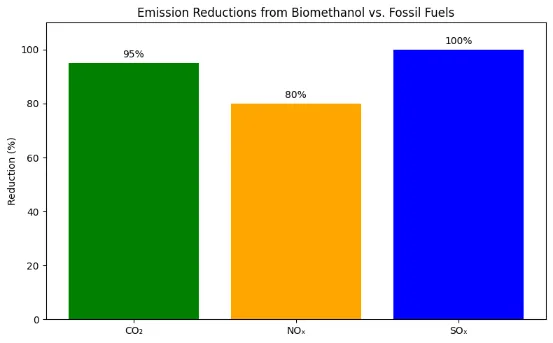
Biomethanol is a renewable form of methanol produced from sustainable biomass sources such as agricultural and forestry residues, municipal solid waste (MSW), biogas, sewage, and industrial by-products like black liquor from the pulp and paper industry. Unlike conventional methanol, which is derived from fossil fuels, biomethanol offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and plays a crucial role in decarbonizing various industrial and energy sectors.
Key Investment Highlights
- Up to 95% reduction in CO₂ emissions compared to fossil fuels
- Versatile applications across multiple industries
- Supports circular economy through waste valorization
- Compatible with existing fuel infrastructure
- Strong regulatory support worldwide
Market Size and Growth Projections (2025–2033)
Alternative market estimates value the sector at $91.51 billion in 2025, with a steady CAGR of 3.4% through 2033, indicating robust and sustained demand across different market segments.
Why Invest in Biomethanol Now?
1. Immature Market with Exponential Growth Potential
Biomethanol is at the early phase of market take-up, with first-mover benefits for investors. The industry’s growth potential outclasses most other green fuels, led by regulatory drive and expanding demand for low-carbon alternatives in shipping, transport, and chemicals.
2. Broadening Application Landscape
The diversity of applications is a big plus for biomethanol:
- Fuel: Straight use in internal combustion engines and blending with gasoline
- Feedstock: For manufacture of DME, MTBE, biodiesel, and green hydrogen
- Chemicals: Synthesis of plastics, solvents, and specialty chemicals
- Energy Storage: Power-to-methanol technologies for renewable energy storage
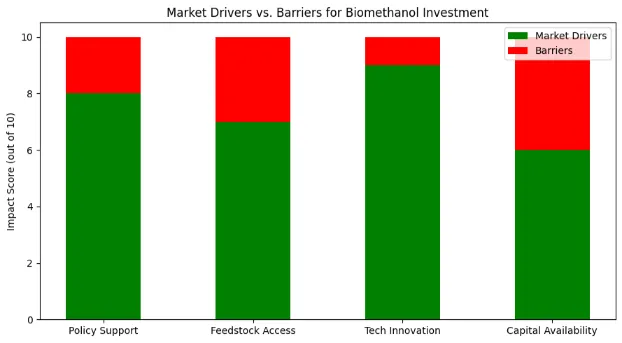
3. Strong Policy and Regulatory Tailwinds
Governments worldwide are enacting stricter emissions standards and offering incentives for renewable fuels. Biofuel blending mandates and carbon pricing mechanisms are accelerating adoption, especially in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
4. Technological Innovation
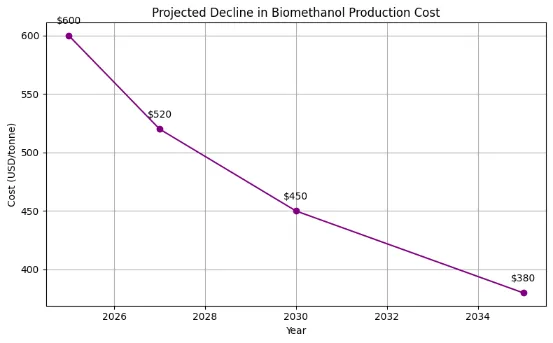
Recent advancements enable use of diverse feedstocks including agricultural waste, MSW, and captured CO₂. Innovations in gasification, fermentation, and catalysis are driving down costs and improving yields.
5. Circular Economy Benefits
Biomethanol production from waste streams addresses critical waste management challenges while creating renewable fuel, aligning with circular economy principles and creating additional revenue streams.
Key Players and Regional Opportunities
Industry Leaders
- BioMCN
- Carbon Recycling International
- Enerkem
- BASF
- Methanex
- Glocal Green
These firms are expanding production capacities, developing new technologies, and forming strategic partnerships to accelerate market penetration.
Regional Hotspots for Growth
| Region | Status & Prospects |
|---|---|
| North America | Leading in infrastructure and policy support; strong growth in the US and Canada |
| Europe | Early adoption, robust regulatory environment, especially in Scandinavia and Germany |
| Asia-Pacific | Fastest projected growth, driven by population, industrialization, and government sustainability focus |
Production Technologies
Biogas Route
Easiest to implement but currently higher cost due to scale limitations. Offers moderate carbon intensity reduction and potential for carbon capture during upgrading.
MSW & Biomass Gasification
Solves waste disposal issues and benefits from tipping fees. Rapid developments are ongoing, with green premiums due to high demand and limited supply.
Glycerol Steam Reforming
Offers some of the lowest carbon intensities and competitive costs in select locations, though currently less widespread.
Integration with E-Methanol
Power-to-methanol technologies combine renewable electricity with CO₂ and hydrogen, enabling further decarbonization of the fuel supply chain.
Challenges and Risks
- Feedstock Availability: Sustainable supply of waste biomass and MSW is crucial for scaling production
- Production Costs: Remain higher than fossil-based methanol, often requiring policy support
- Policy Inconsistencies: Varying regulatory frameworks create uncertainty
- Supply Chain Bottlenecks: Infrastructure for feedstock collection needs scaling
Market Outlook
Biomethanol is poised to become a linchpin in the global transition to a low-carbon economy. Its role in decarbonizing transportation, chemicals, and energy storage makes it indispensable for meeting net-zero targets.
M&A Activity
The industry has seen approximately $500 million in M&A activity over the past five years, with consolidation expected to increase as companies seek scale and technological edge.
Actionable Investment Steps
- Identify Innovative Startups: Focus on advanced feedstock technologies and waste-to-fuel solutions
- Monitor Policy Developments: Track regions with new biofuel mandates and incentives
- Evaluate Partnerships: Look for alliances with established chemical/energy companies
- Assess Feedstock Security: Prioritize projects with reliable long-term feedstock access
- Consider M&A Opportunities: Watch for consolidation trends among innovative players
Conclusion
The biomethanol sector in 2025 offers a rare convergence of sustainability, technological innovation, and market momentum. Early-stage investors who act now stand to benefit from exponential growth, robust policy support, and expanding applications. As the world races toward net-zero emissions, biomethanol is set to play a central role in powering the green economy of the future.