The Trillion Dollar Shift: How Biomethanol Is Poised To Dominate
The Trillion Dollar Shift: How Biomethanol Is Poised To Dominate
Revolutionary renewable energy transformation reshaping global markets
The Trillion Dollar Shift: How Biomethanol Is Set to Take Over
Exploring the renewable fuel revolution that’s reshaping global energy markets
The global energy sector is undergoing a significant change. Renewable fuels are becoming essential for a sustainable future. Among these, biomethanol stands out as a key player, likely to cause a trillion-dollar shift in the way industries, transportation, and economies generate power. As the world speeds up its move away from fossil fuels, biomethanol is quickly gaining popularity as a low-carbon alternative that could reshape markets and provide important environmental benefits.
What Is Biomethanol?
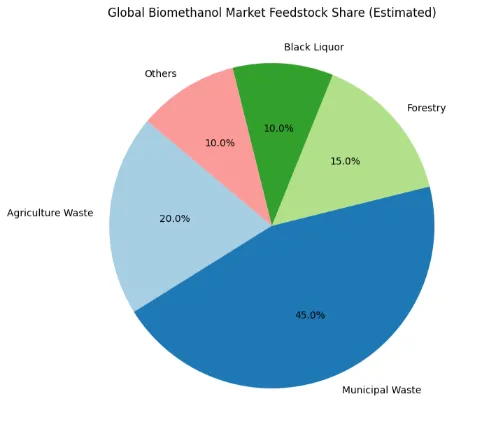
Biomethanol is a renewable version of methanol made from sustainable biomass sources. These sources include agricultural leftovers, forestry waste, municipal solid waste, sewage, and even industrial by-products like black liquor from the pulp and paper industry. Unlike traditional methanol, which comes from fossil fuels, biomethanol has a much lower carbon footprint. This makes it crucial for global efforts to reduce carbon emissions.
Market Growth: The Trillion Dollar Opportunity
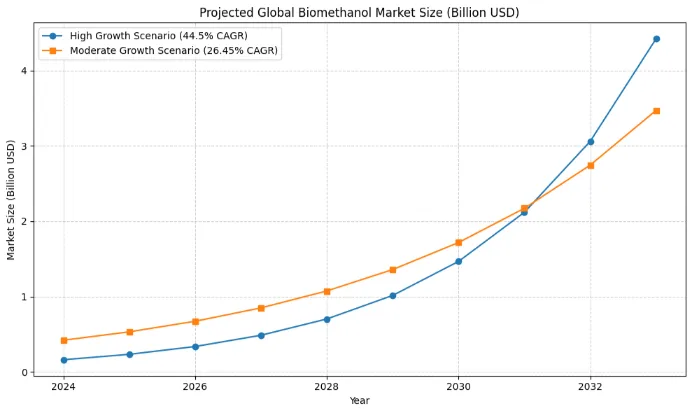
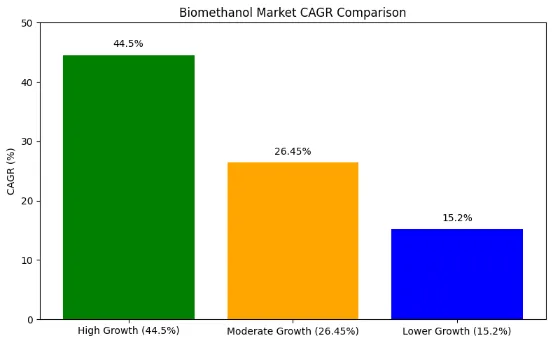
The biomethanol market is growing rapidly. Valued at $161.12 million in 2024, it is expected to rise to $2,118 million by 2032, showing an incredible compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 44.5%. Broader estimates suggest that the biomethanol fuel market could reach $35 billion by 2033, while the overall renewable methanol market may hit $20.68 billion by 2030. Some forecasts even predict the global biomethanol market could reach $86,150 million by 2033.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Clean Fuels: Increasing global awareness of climate change and the need to lower greenhouse gas emissions are driving industries and governments to find sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels.
Supportive Government Policies: Tough environmental rules and incentives are boosting investment in biofuels, including biomethanol.
Technological Advances: New developments in biomass gasification, carbon capture, and advanced catalytic processes are making biomethanol production more efficient and affordable.
Versatile Applications: Biomethanol can be used as a feedstock for biofuels, green chemicals, and synthetic materials. It can also be used directly as fuel or blended with gasoline to lower emissions.
Why Biomethanol? The Unique Advantages
1. Environmental Impact
Biomethanol has a much smaller carbon footprint compared to fossil-derived methanol. Its life-cycle emissions are greatly reduced, especially when made from waste materials or used with carbon capture and storage technologies.
2. Versatility Across Sectors
Transportation: Biomethanol can be used as a direct fuel, a gasoline additive, or in biodiesel production, making it important for cleaner road and maritime transport.
Chemicals: Biomethanol is a key ingredient for making acetic acid, formaldehyde, plastics, and other green chemicals.
Energy Storage: With its high energy density and easy storage, biomethanol is being explored as an alternative energy carrier that competes with hydrogen in the developing “Methanol Economy.”
3. Circular Economy and Waste Valorization
By turning municipal solid waste, agricultural leftovers, and other biomass into valuable fuel, biomethanol supports circular economy models and cuts down on landfill use.
4. Compatibility and Infrastructure
Biomethanol can fit into existing fuel systems. It can be used in current engines with minor adjustments and blended with gasoline in various ratios (M10, M15, M85), making it easy for users to transition.
Technological Innovations Fueling Growth
Advanced Gasification & Biorefineries
Modern biorefineries are using advanced gasification methods to convert a variety of feedstocks into biomethanol efficiently. This boosts yields and allows for the use of otherwise hard-to-recycle waste.
Carbon Capture and Utilization
Combining carbon capture and storage (CCS) and direct air capture (DAC) technologies makes biomethanol production even more sustainable. This process uses captured CO₂ as a feedstock, further lowering emissions.
Emerging Production Pathways
New catalytic processes and direct gas fermentation are being created to cut costs and enhance scalability, positioning biomethanol as a truly global option.
Market Segmentation and Regional Trends
By Application
Fuel Blending: The biggest segment is driven by regulations aimed at cutting vehicle emissions and the need for cleaner transportation fuels.
Chemical Manufacturing: Used for creating plastics, formaldehyde, and other chemicals.
Energy Storage and Power Generation: Gaining popularity as an alternative to hydrogen and natural gas.
By Region
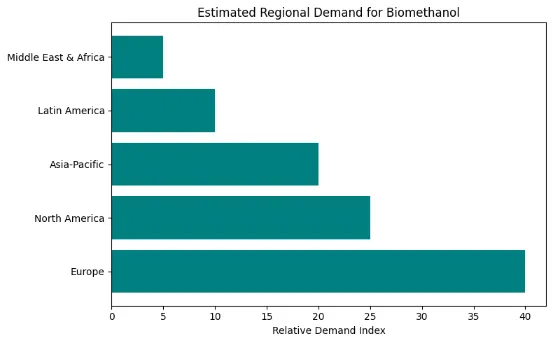
North America & Europe: Leading the way in adoption, thanks to strong policy support and established biofuel markets.
Asia-Pacific: Set for rapid growth due to rising energy needs, significant investments in renewables, and growing environmental awareness, particularly in China and India.
Emerging Markets: Developing countries are starting to invest in biomethanol infrastructure, recognizing its potential to bypass fossil-based energy systems.
Challenges and Barriers
Despite its potential, biomethanol faces several challenges:
High Production Costs: It is currently more expensive to produce biomethanol than fossil-based methanol. This is mainly due to high feedstock costs and the expensive nature of advanced biorefineries.
Feedstock Availability: Sourcing biomass sustainably at scale remains a challenge, especially in areas with limited agricultural or forestry waste.
Infrastructure Needs: Large-scale use requires strong logistics, storage, and distribution networks, which are still developing in many places.
Competition: Biomethanol competes with other biofuels, like biodiesel, and emerging technologies such as hydrogen and electric vehicles.
However, as economies of scale are realized and technologies advance, production costs are expected to drop, making biomethanol more competitive.
The Path Forward: What Will Drive Biomethanol’s Dominance?
1. Policy and Regulation
Continuing to tighten emissions limits, carbon pricing, and government incentives will be essential for speeding up biomethanol adoption.
2. Industry Collaboration
Partnerships among technology providers, chemical manufacturers, energy companies, and governments will foster innovation and investment, helping to tackle infrastructure and cost challenges.
3. Consumer and Corporate Demand
As sustainability becomes a key value for consumers and companies, demand for low-carbon fuels like biomethanol will continue to grow, especially in sectors where electrification is difficult (like shipping, aviation, and heavy industries).
4. Technological Breakthroughs
Ongoing research and development in feedstock processing, gasification, and carbon capture will make biomethanol even more cost-effective and scalable.
Case Studies: Biomethanol in Action
Maritime Shipping: Major shipping companies are testing biomethanol as a marine fuel to meet International Maritime Organization (IMO) targets for reducing sulfur and carbon emissions.
Urban Waste-to-Fuel: Cities are converting municipal solid waste into biomethanol to cut down on landfill use and create local renewable energy.
Green Chemicals: Chemical manufacturers are shifting to biomethanol-based feedstocks to lower their carbon impact and comply with regulations.
Conclusion: The Dawn of the Biomethanol Era
The world is on the brink of a trillion-dollar shift, with biomethanol likely to become a key part of the global energy and chemical sectors. Its unique mix of versatility, environmental benefits, and compatibility with current systems makes it a standout option for the clean energy transition. As technology improves and policy support grows, biomethanol is set to take center stage in the renewable fuels market, leading a new era of sustainable growth and climate resilience.
Ready to Learn More About Renewable Energy?
Stay updated with the latest developments in biomethanol and sustainable energy solutions. Join our community of forward-thinking energy professionals and environmental advocates.